In SAP ERP Central Component, SAP FICO is a crucial core functional element that enables an organization to handle all of its financial data. Any business can store a complete copy of their financial transaction data using SAP FICO. SAP FICO Training In Hyderabad is one of the most sought out courses in Hyderabad due to the huge demand of SAP FICO Consultants.
If you are looking for career guidance on which SAP Course to choose then contact us on [email protected] or here. One of our representative will get in touch with you in 24 hours.
SAP FICO is specifically designed to assist businesses in producing and managing financial statements for analysis and reporting as well as supporting efficient business planning and decision-making.
First Bridge Consulting is an industry pioneer in SAP FICO Course by providing Instructor-Led by the Industry experts who have over 12 to 15 years of experience in the field of SAP FICO.
What Is SAP FICO Full Form
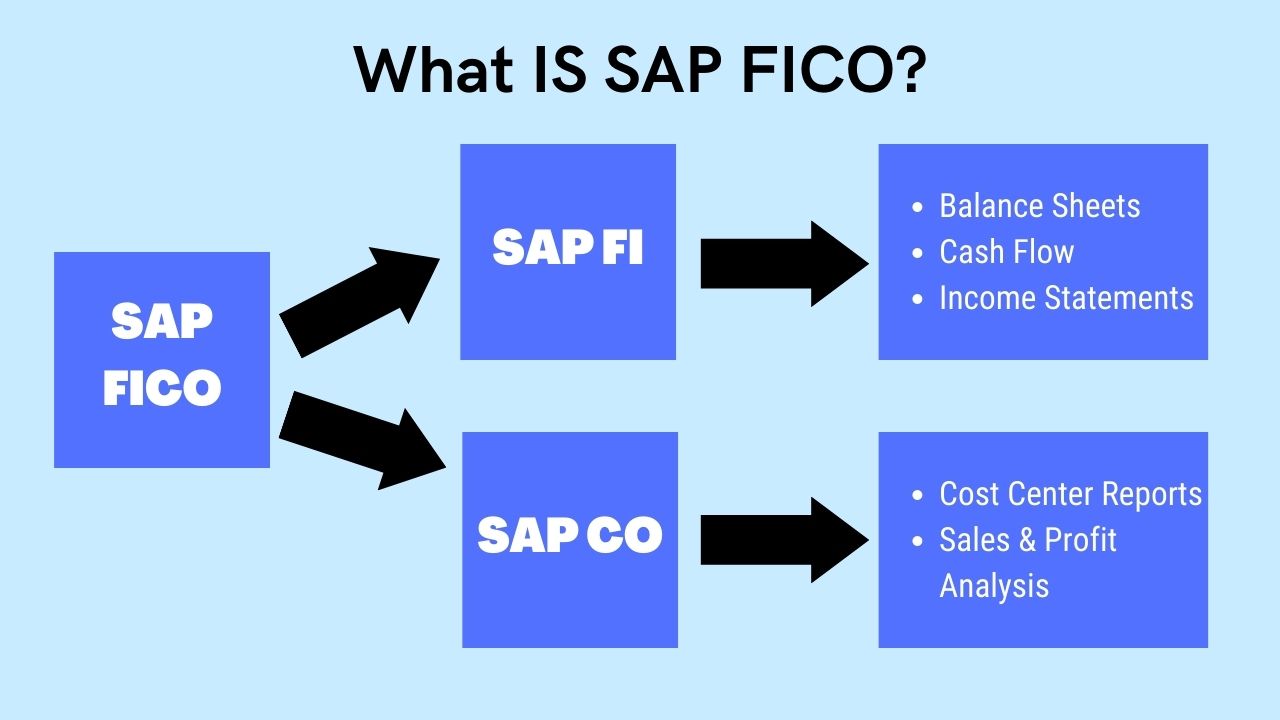
The SAP FICO full form is FI (Financial Accounting) and CO (Controlling).
SAP FICO In Depth
There are two sections in SAP FICO: SAP Finance (FI) and SAP Controlling (CO). Each of which is employed in a particular financial procedure. While SAP CO focuses more specifically on cost planning and monitoring, SAP FI works with total financial reporting and accounting. Despite being first introduced as different modules, SAP FI and SAP CO are now so closely interwoven that many people just refer to them as one module.
Other SAP Logistics modules, such as Sales and Distribution (SD), Production Planning (PP), Plant Maintenance (PM), Quality Management (QM), and Materials Management(MM), can also integrated with SAP FICO.
SAP FI Module
Financial statements can be created by enterprises using SAP FI for reporting and analysis. Balance sheets and profit and loss statements are two examples of financial statements. The following sub-modules of SAP FI deal with particular accounting processes:
- All of the company’s transactional information is organised on a chart of accounts in the general ledger. This contains a list of each account in the database. Sub-modules that can be updated in real time with general ledger data are used to record transactions.
- Customer transactions are recorded and customer accounts are managed through accounts receivable. The execution of customer reports, invoice posting, credit memo posting, down payments, and invoice payments are all examples of transactions.
- All interactions with vendors and controlled vendor accounts fall under the category of accounts payable. Invoice posting, credit memo posting, down payments, invoice payments, automatic payments programme, and executing vendor reports are just a few examples of transactions.
- Asset accounting oversees all of the business’s fixed assets, such as real estate, construction projects, and large pieces of machinery. Asset purchases, retirement, sales, transfers, revaluations, and depreciation are all examples of transactions.
- All bank account activity and information for the company are handled by the bank ledger. It can check all transactions in the system with those on bank statements to reconcile them.
- By combining the financial accounts of many businesses through consolidation, the company can get a comprehensive picture of its overall financial situation.
- The company’s revenue and cost budgets are managed by Funds Management.
- The SAP FI ledgers are defined by Special Purpose Ledger for reporting needs.
- Booking trips and managing travel-related expenses are only a few of the transactions that Travel Management manages.
SAP CO Module
SAP CO supports processes to plan, report on, and monitor costs associated with business operations, in contrast to SAP FI, which deals with an organization’s accounting and internal and external reporting. SAP CO can play a key role in raising business profitability. Like SAP FI, SAP CO is made up of sub-modules that deal with particular processes:
- Cost Elements, based on profit and loss statements, also known as income statements, gives a broad picture of all the company’s costs and revenues. The genesis of the costs is described by cost element accounting. Cost factors are distinct expenses that the business has.
- The expenditures related to the organization’s internal divisions or departments, such as sales, production, marketing, or human resources, are dealt with by cost centres. Cost centres only include expenses; they exclude revenues.
- All cost information pertaining to the company’s business lines is handled by profit centres. In contrast to Cost Centers, which solely deal with expenses, it deals with both expenses and income.
Smaller internal projects or non-fixed assets, such as a temporary marketing campaign, are managed using Internal Orders. - The business can evaluate the profitability of its products thanks to profitability analysis. Profitability analysis, for instance, can be helpful when deciding on issues like product pricing, distribution methods, and target market segments. Additionally, it enables several levels of granularity in the analysis of profitability, such as for every country, type of product, and route of distribution, or profitability for each individual client.
- Data about the expenses incurred in producing the company’s products and services is managed through product costing. Analyzing product costs can assist manage production costs and maximise efficiencies.
SAP FICO Course Content
Module 1: General Ledger Accounting
- General Ledger Master
- General Ledger Postings
- General Ledger Parking and postings
- Reversals
- Automatic Clearing
- Recurring Entries
- Taxes
- General Ledger Reports
Module 2: Cash and Bank Accounting
- Cash Journals
- Cheque Management
- House bank Masters
- Bank Reconciliations
Module 3: Accounts Payable
- Vendor Master
- Vendor Invoice Posting
- Vendor Credit Memo
- Vendor Down Payment
- Vendor Down Payment Clearing
- Vendor Outgoing payment
- Partial payment against an invoice
- Residual Payment
- Automatic Payment Run
- Withholding Tax (TDS)
- Vendor Reports
Module 4: Accounts Receivable
- Customer Master
- Customer Invoice Posting
- Customer Credit Memo
- Customer Down Payment
- Customer Down Payment Clearing
- Customer Incoming Payment
- Partial payment against an invoice
- Residual Payment
- Customer Reports
Module 5: Asset Accounting
- Asset Master
- Asset Procurement (Direct)
- Asset Procurement (through MM)
- Asset Retirements
- Asset Scrapping
- Depreciation Run
Module 6: SAP FI Consultant Level:
- Define a Company
- Define a Company Code
- Assign Company Code to Company
- Define Chart of Accounts
- Assign Company Code to Chart of Accounts
- Setup Account Groups and their Number Ranges
- Assign Fiscal Year Variant to Company Code
- Assign Posting Period Variant to Company Code
- Document Number Ranges for the Company Code
- Assign Field Status Variant to Company Code
- Define Employee Tolerance
- Define Retained Earnings Account
- Document types
- Posting Keys
- Validation and substitution
- General Ledger Account Introduction
- Reconciliation Accounts
- Expense and Revenue GL Accounts
- Account Assignment Model
- Setup tolerance for customers and vendors
- Customer Account Groups
- Create number ranges for customer accounts
- Assign number ranges to customer groups
- Customer Master Record
- Create Vendor Groups
- Create number ranges for vendor accounts
- Assign number ranges to vendor groups.
- Create Vendor Master
- Create underpayment account and Over payment accounts
- Create cash discount account
- Payment within tolerance (incoming)
- Payment within tolerance (outgoing)
- Configure Automatic Payment Program
- Financial Statement Version
- Cash Journals
- House Bank Configuration
- Check Management
- Manual Bank Reconciliation
- Asset Masters
- Asset Number Ranges
- Depreciation Areas
- Asset General Ledger Account Determination
- Depreciation Keys
- NEW GL and Document Splitting concepts